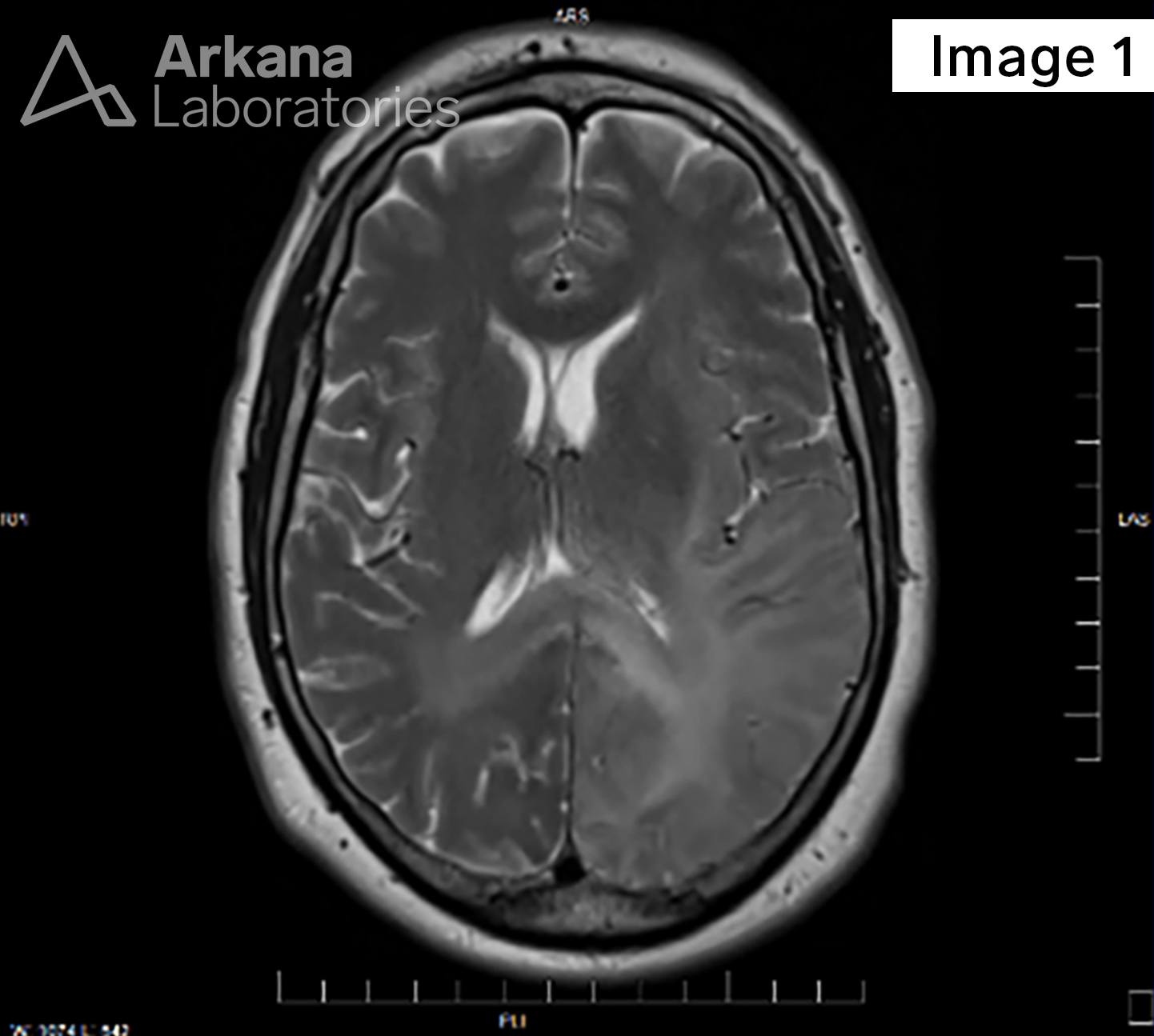
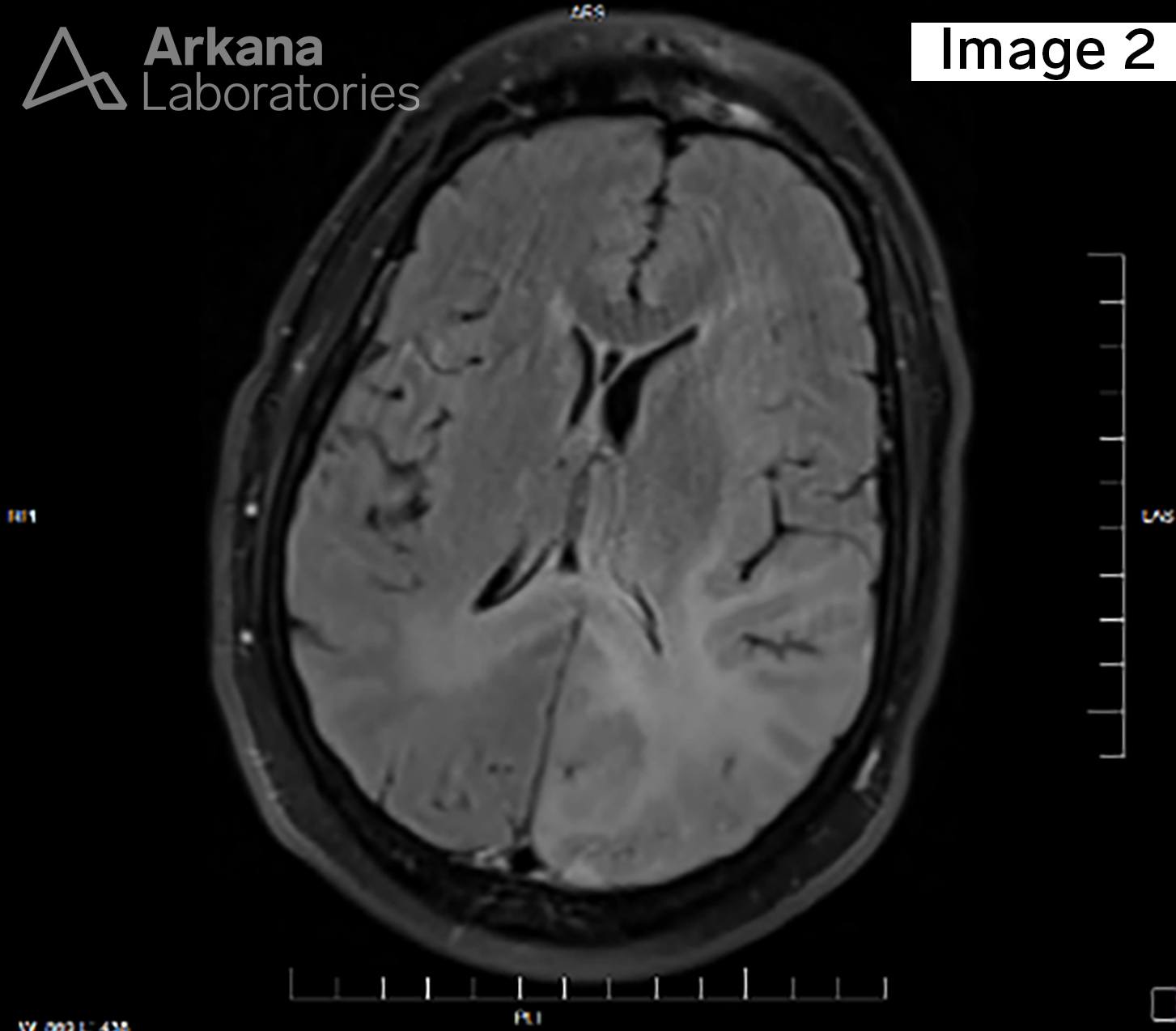
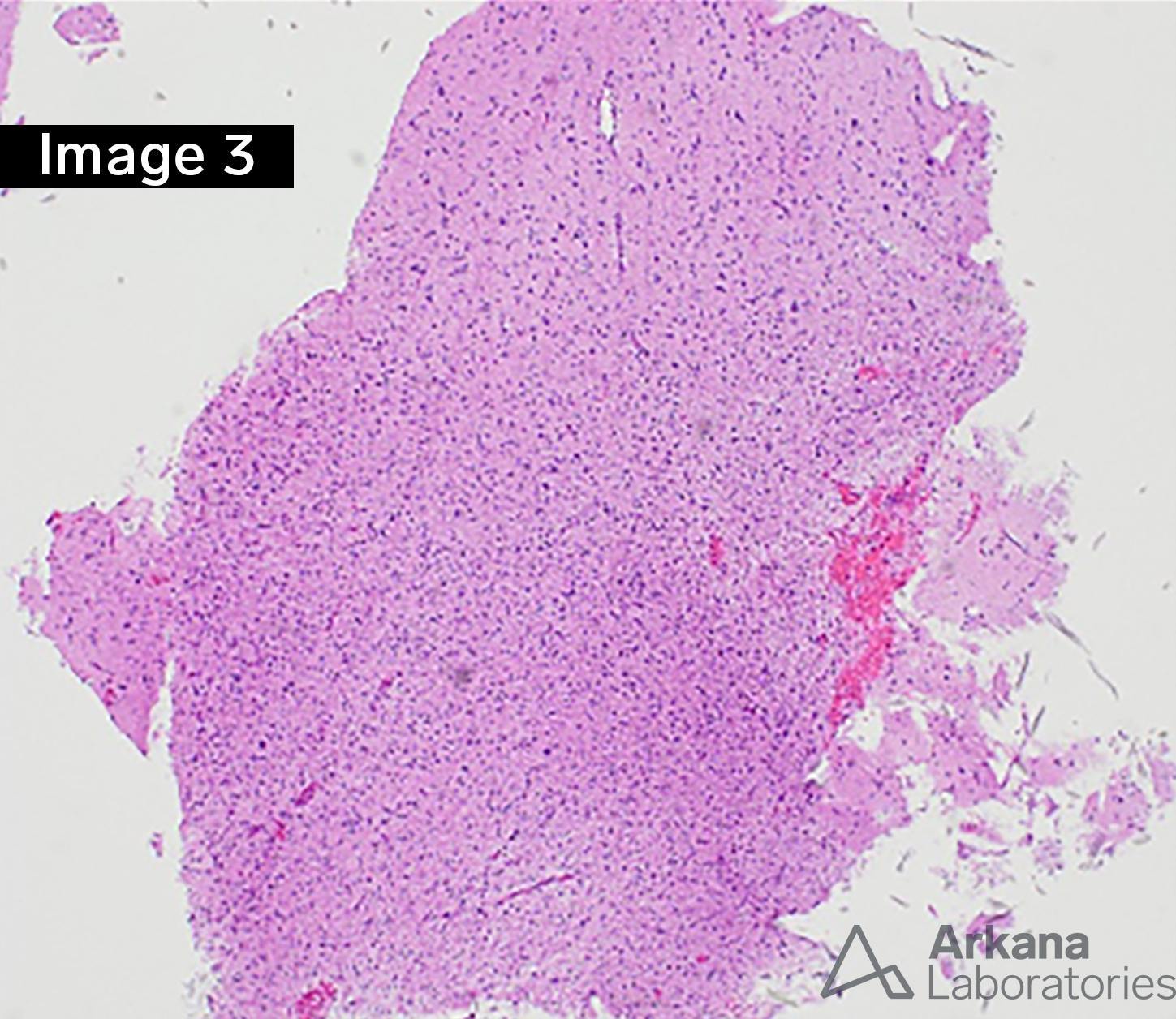
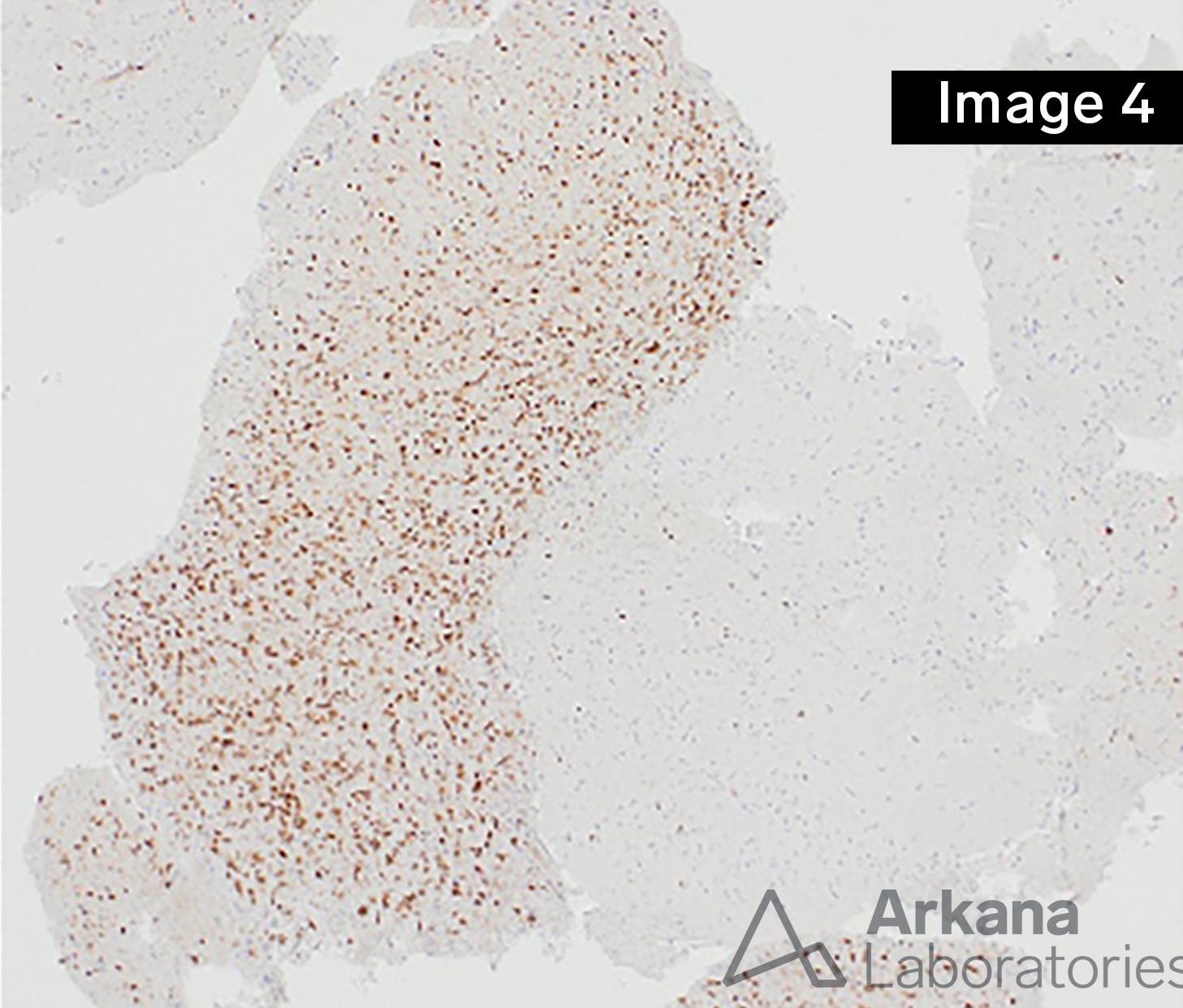
The field of neuropathology is currently in a state of exponential growth and increased understanding of the pathogenesis of brain tumors, which has been heralded in the literature by the Consortium to Inform Molecular and Practical Approaches to CNS Tumor Taxonomy, Not Official WHO (cIMPACT-NOW) working groups. For example, in this case of a diffusely infiltrating glioma in an adult patient, MRI neuroimaging shows mild T2 hyperintensity and increased FLAIR signal in the left parietal-occipital lobes with extension across the midline at the genu of the corpus callosum (Figures 1 and 2, respectively). Stereotactic brain biopsy with neuronavigation yields hypercellular brain tissue involved by a histologically lower-grade diffuse-type astrocytoma with a very rare mitotic figure without microvascular proliferation or necrosis (Figure 3, H&E stain, 100x). Immunohistochemical (IHC) stain work-up confirms that the astrocytoma is IDH-mutant (Figure 4, IDH1-R132H immunostain, 40x) with strong p53 immunoreactivity, loss of ATRX, and shows a mild elevation in Ki-67 proliferative index (IHC stains not shown), as well as negative for codeletion of 1p/19q by FISH. Using the current 2016 WHO of CNS Tumours, revised 4th edition, this tumor would be diagnosed as, “Diffuse astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, WHO grade II.” The cIMPACT-NOW update 5 literature has recognized molecular diversity within this group of IDH-mutant astrocytomas, and has also advocated for using molecular data in establishing an overall grade. However, incorporating the cIMPACT-NOW proposed terminology, this tumor would be classified as “Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant, grade 2,” as analysis for CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion is negative by FISH. Concern for partial sampling of a higher grade lesion may be stated in a comment. For more details on the ongoing progress in surgical oncologic neuropathology, please see the reference below.
Reference:
Brat DJ, Aldape K, Colman H, et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 5: recommended grading criteria and terminologies for IDH-mutant astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;139(3):603-608.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.