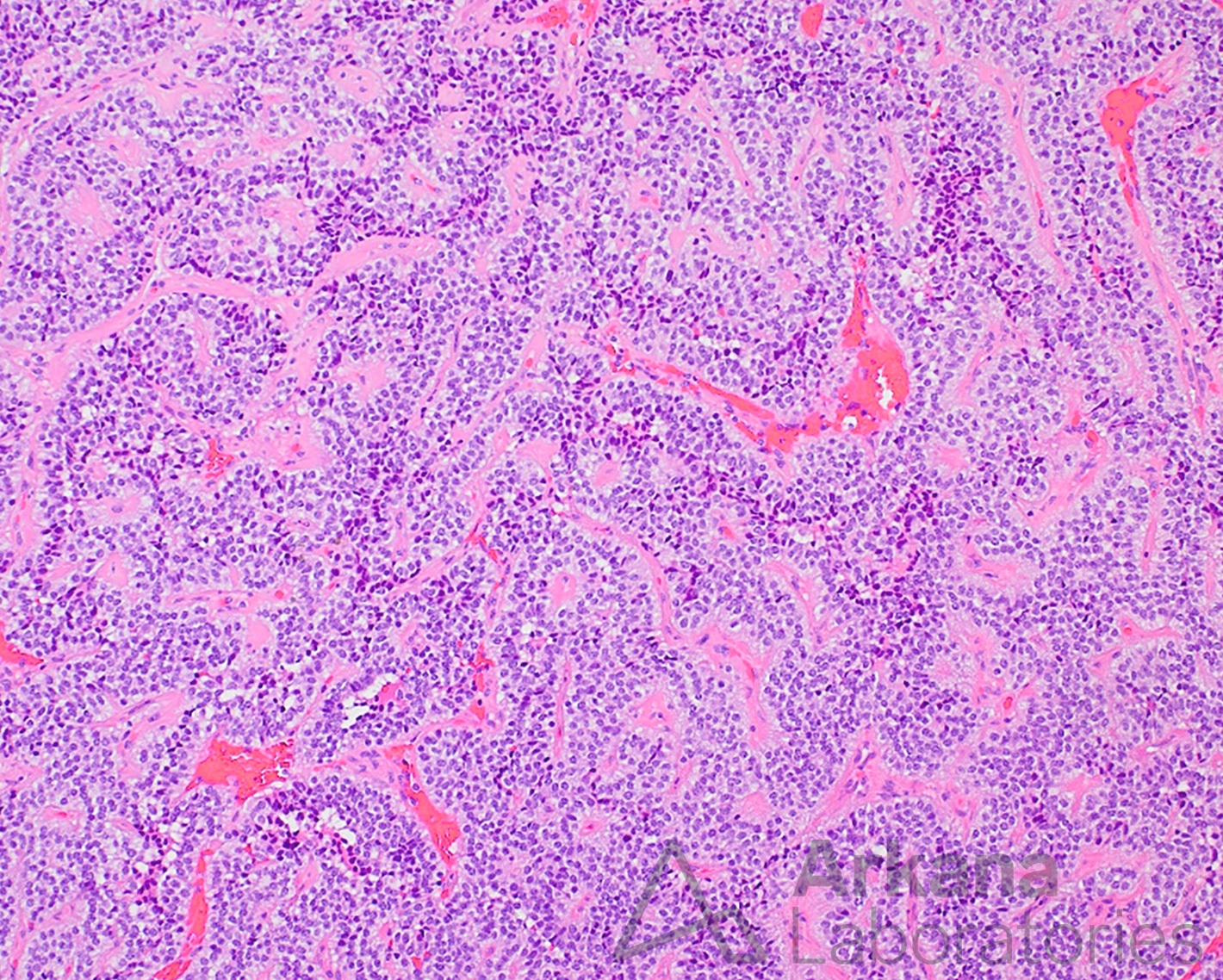
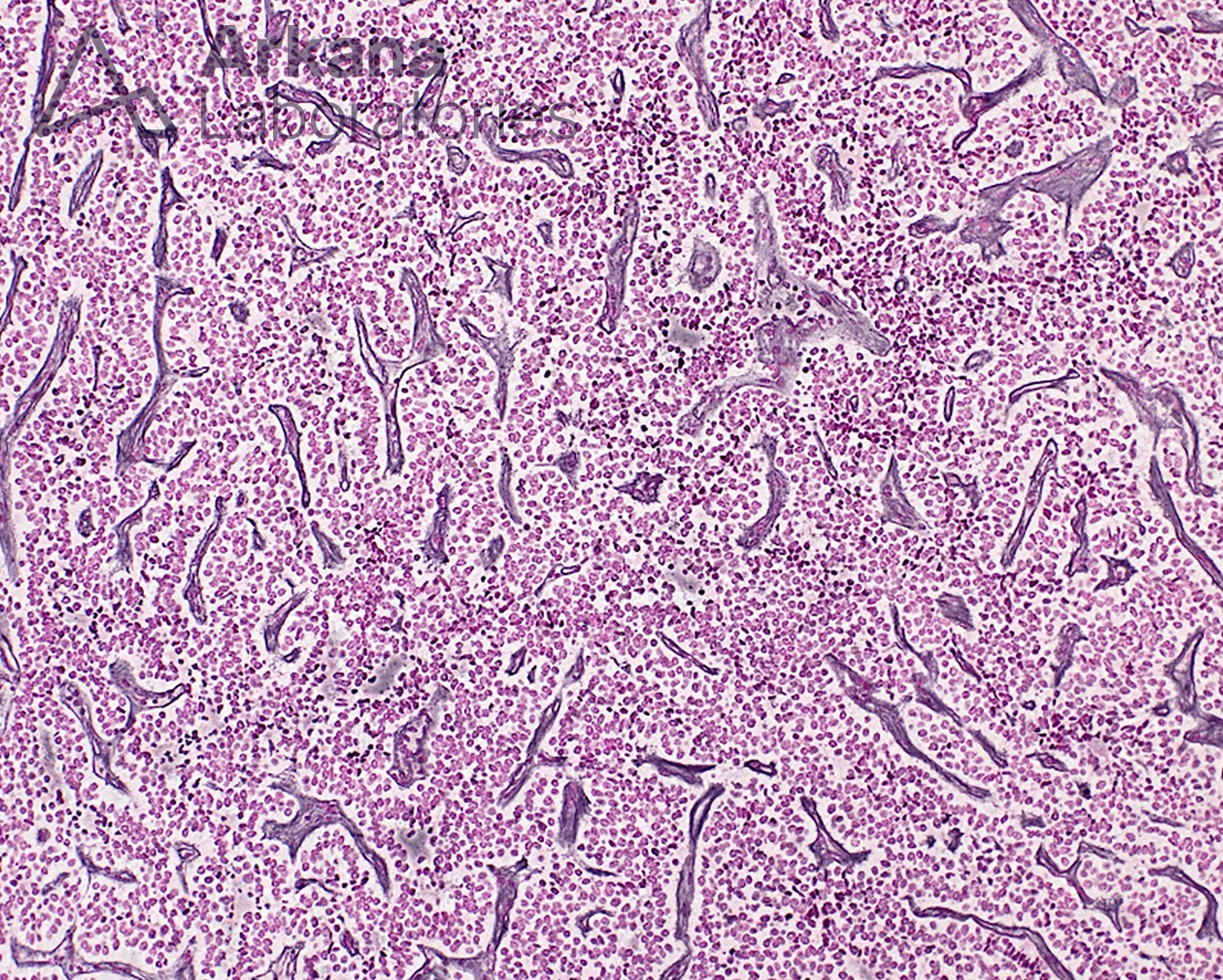
The patient is an obese middle-aged male who presents with complaints of headaches, vision changes, and loss of libido. Neuroimaging reveals a 2 cm sellar mass. Endocrinology work-up shows no significant elevation in prolactin, ACTH, or growth hormone, and thyroid panel is within normal limits. The decision was made to pursue endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal resection of the pituitary macroadenoma. Neuropathology microscopic examination shows a primary pituitary neoplasm arranged in a papillary growth pattern with patchy immunoreactivity for FSH greater than LH, and alpha subunit of the glycoprotein hormones (FSHα).
Using the images, which of the following pituitary gland transcription factors is positive in this case?
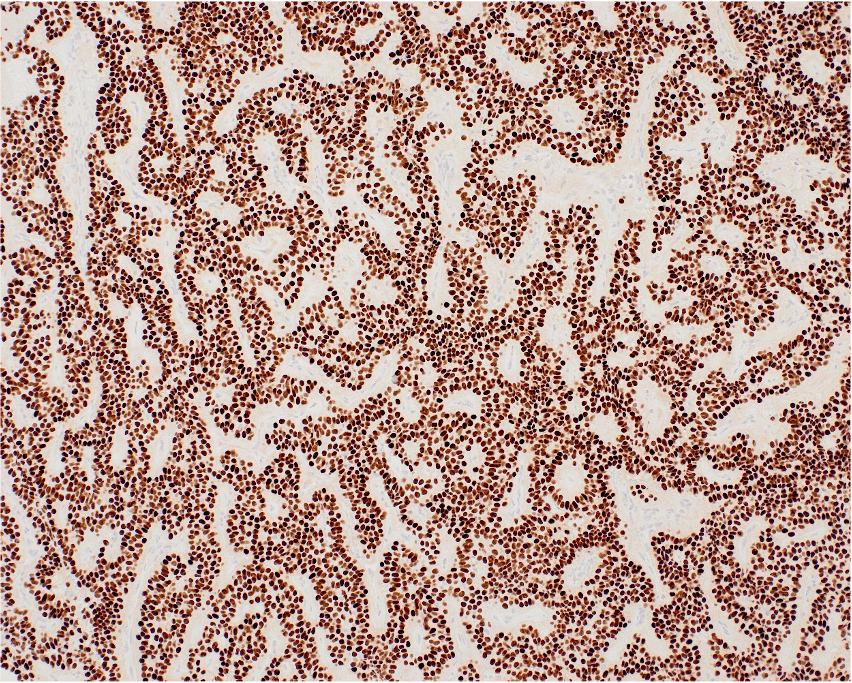
Immunohistochemical (IHC) stain for the transcription factor steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) shows strong diffuse immunoreactivity in this gonadotroph adenoma with a papillary growth pattern. Original magnification: 100x.
Answer: Gonadotroph Adenoma SF-1
This case demonstrates a gonadotroph adenoma, immunopositive for SF-1. Recent classification schemes have incorporated the relevance of lineage-restricted pituitary gland transcription factors into three basic lineages: Pit-1 (pituitary specific transcription factor), T-pit (T-box transcription factor), and SF-1 (steroidogenic factor-1).
SF-1 delineates gonadotroph adenomas (βFSH, βLH, and α-su, in various combinations). The Pit-1 lineage defines lactrotroph, somatotroph, and thyrotroph adenomas. The T-pit lineage characterizes corticotroph adenomas.
TTF-1 (thyroid transcription factor-1) is mostly commonly used in the work-up of pulmonary adenocarcinoma, but is also used to define posterior pituitary gland tumors (i.e. spindle cell oncocytoma (SCO) of the pituitary gland).
References
Asa SL, Casar-Borota O, Chanson P, et al; attendees of 14th Meeting of the International Pituitary Pathology Club, Annecy, France, November 2016. From pituitary adenoma to pituitary neuroendocrine tumor (PitNET): an International Pituitary Pathology Club proposal. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017 Apr;24(4):C5-C8. PMID: 28264912.
Giantini Larsen AM, Cote DJ, Zaidi HA, Bi WL, Schmitt PJ, Iorgulescu JB, Miller MB, Smith TR, Lopes MB, Jane JA, Laws ER. Spindle cell oncocytoma of the pituitary gland. J Neurosurg. 2018 Oct 19;131(2):517-525. PMID: 30485213.
Lopes MBS. The 2017 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the pituitary gland: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2017 Oct;134(4):521-535. PMID: 28821944.
McDonald WC, Banerji N, McDonald KN, et al. Steroidogenic Factor 1, Pit-1, and Adrenocorticotropic Hormone: A Rational Starting Place for the Immunohistochemical Characterization of Pituitary Adenoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017 Jan;141(1):104-112. PMID: 27227698.
McDonald WC, McDonald KN, Helmer JA, et al. The Role of T-box Transcription Factor in a Pituitary Adenoma Diagnostic Algorithm. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021 May 1;145(5):592-598. PMID: 32991684.
Osamura, R.Y.; Grossman, A.; Korbonits, M.; Kovacs, K.; Lopes, M.B.S.; Matsuno, A.; Trouillas, J. Pituitary adenoma. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs; Chapter 1: Tumors of the Pituitary Gland; WHO: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 14–18.
Trouillas J, Jaffrain-Rea ML, Vasiljevic A, Raverot G, Roncaroli F, Villa C. How to Classify the Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNET)s in 2020. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 22;12(2):514. PMID: 32098443
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.