This 55-year old patient presented with a two-year history of proximal lower extremity weakness, difficulty grasping objects and atrophy of intrinsic hand muscles. CPK levels were within normal limits. Their family history was negative for neuromuscular disease. Hematoxylin and eosin stained sections from this patient’s muscle biopsy demonstrated morphologic alterations of an acquired inflammatory myopathy with a polymyositis-like pattern of inflammation and muscle fiber injury. Scattered muscle fibers containing single to multiple rimmed vacuoles were present.
What is the Thioflavin T stain highlighting?
A. Nuclei
B. Mitochondria
C. Fibrillary inclusions
D. Cytoplasmic bodies
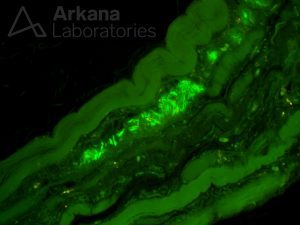
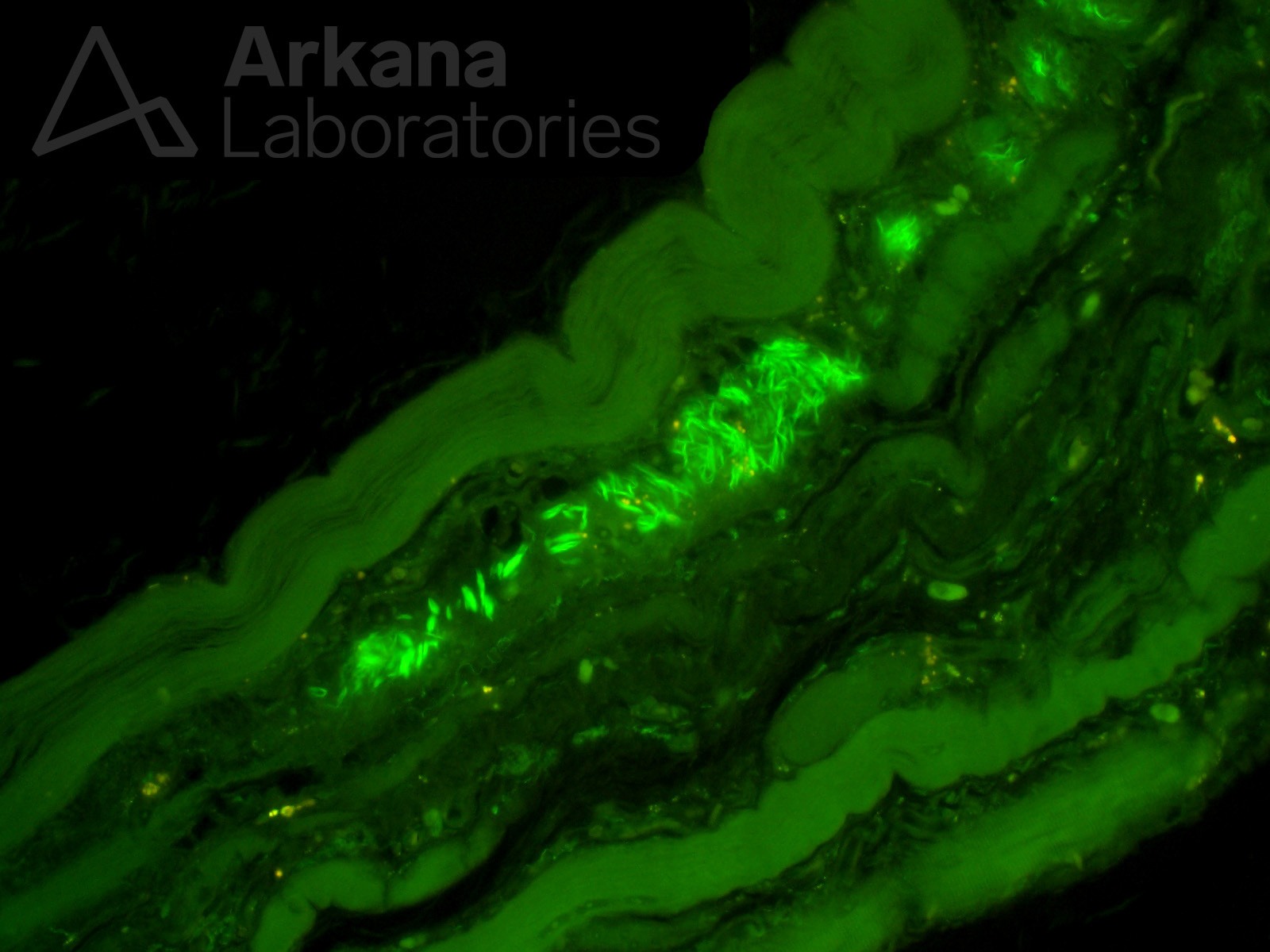
Figure 1: Thioflavin T stain 400x original magnification
Answer: Fibrillary inclusions
The distribution of this patient’s muscle weakness and presence of morphologic changes of an acquired inflammatory myopathy with rimmed-vacuoles are characteristic of sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis (sIBM). The intrasarcoplasmic and/or intranuclear amyloid-like fibrillary inclusions that accumulate in this disease are demonstrated with Congo Red stain (i.e. are congophilic) and show positive reactivity with TDP43 and p62 immunohistochemical stains. Thioflavin T, as shown in this case, also highlights the amyloid-like fibrillary inclusions.
Reference(s)/Additional Reading
Naddaf E, Barohn RJ, Dimachkie MM. Inclusion Body Myositis: Update on Pathogenesis and Treatment. Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Oct;15(4):995-1005. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0658-8. PMID: 30136253; PMCID: PMC6277289.
Greenberg SA. Inclusion body myositis: clinical features and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 May;15(5):257-272. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0186-x. PMID: 30837708.
Groenning M. Binding mode of Thioflavin T and other molecular probes in the context of amyloid fibrils-current status. J Chem Biol. 2010 Mar;3(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s12154-009-0027-5. Epub 2009 Aug 20. PMID: 19693614; PMCID: PMC2816742.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.

