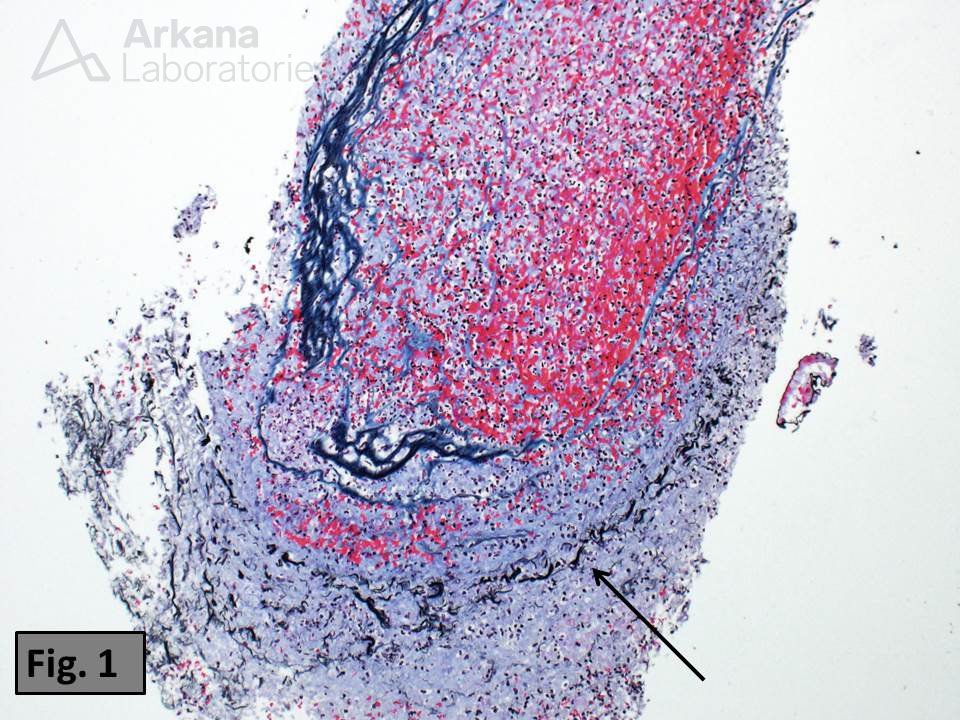
Infective endocarditis can have numerous deleterious effects on the kidney. One such renal complication is the formation of arterial thromboemboli. The renal biopsy images, in this case, are from a 74-year-old man with an artificial heart valve who was being evaluated for acute renal failure. Figure 1 shows an arterial cross section whose elastic laminae are highlighted using a Jones silver stain (see arrow). The artery is distended by intraluminal fibrin and neutrophilic debris, consistent with aseptic thromboembolism.
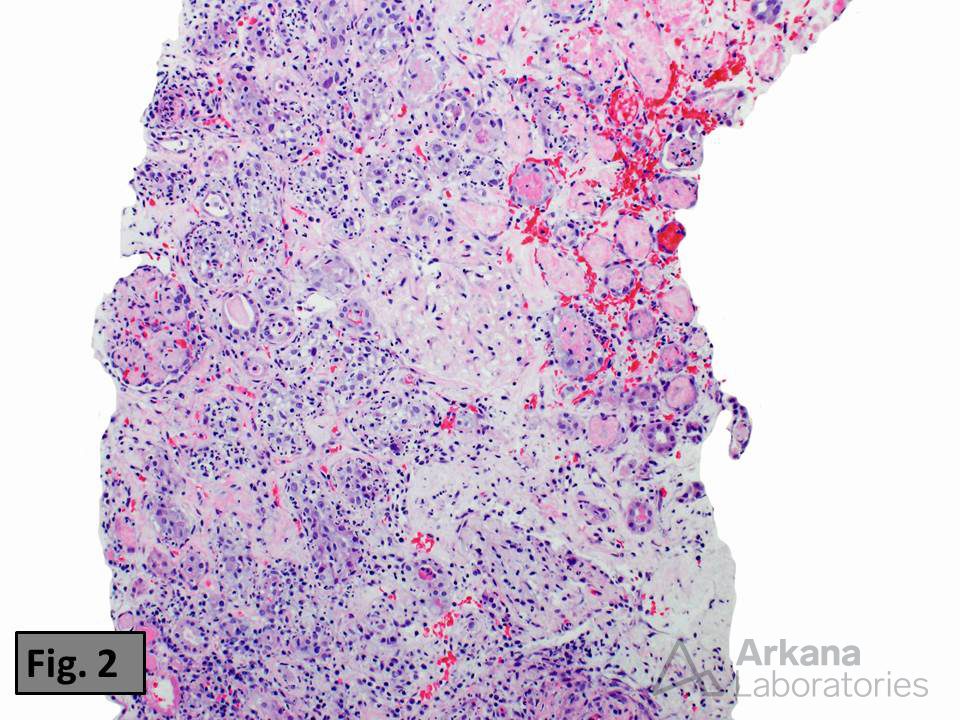
Figure 2 shows the morphologic features of a renal cortical infarct, which was identified in the adjacent cortex.
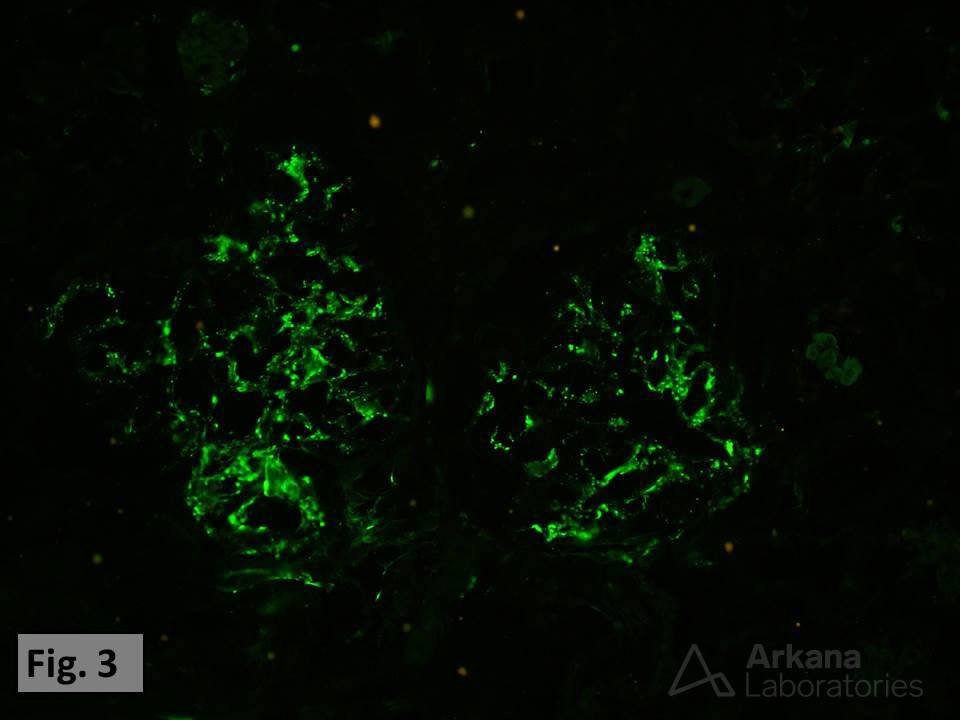
A second complication of infective endocarditis is the development of an immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis. Immunofluorescence studies of the glomeruli from this same biopsy showed diffuse glomerular immune complex deposits (IgA and C3)(Figure 3).
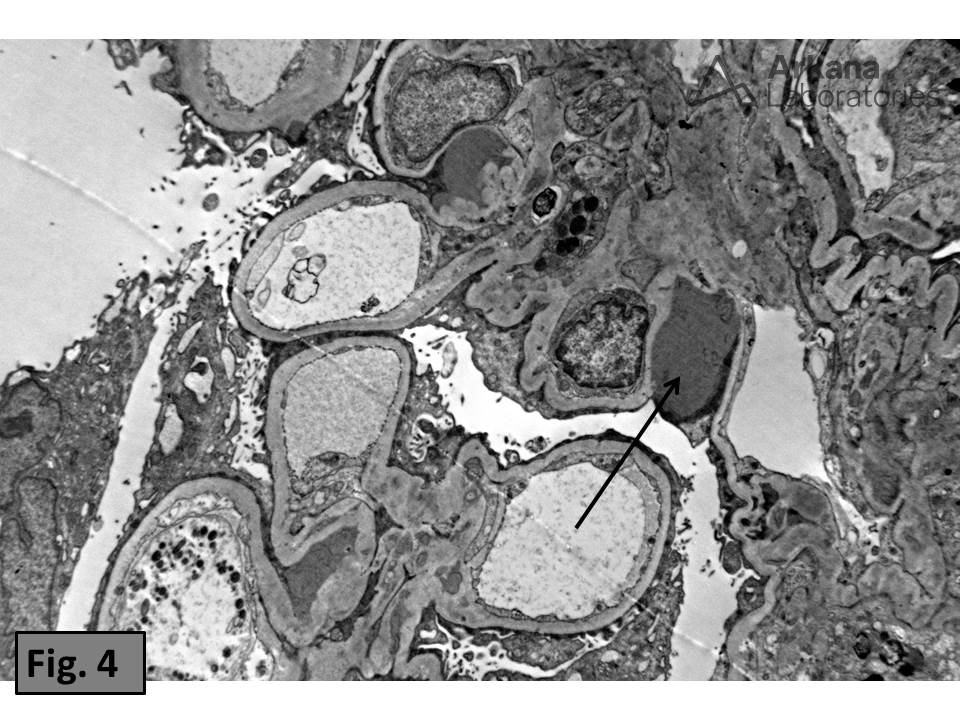
Large paramesangial deposits were confirmed using electron microscopy (Figure 4).
Reference
Boils CL, Nasr SH, Walker PD, Couser WG, Larsen CP. Update on endocarditis-associated glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2015 Jun;87(6):1241-9. PubMed PMID: 25607109
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.