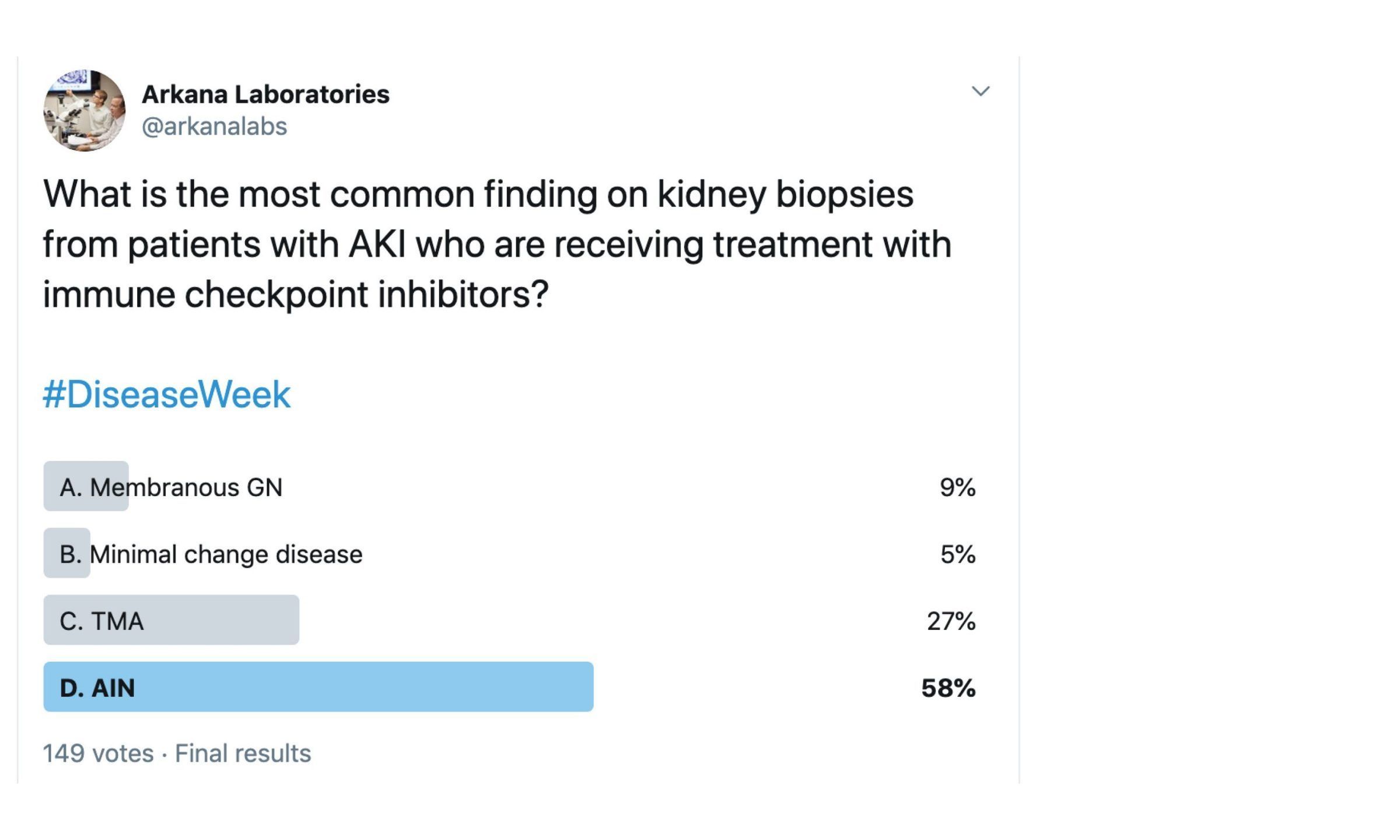
ANSWER: D, AIN
The most common finding on kidney biopsies in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPIs)–induced AKI is acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Less frequently, granulomatous interstitial nephritis and TMA have also been reported.
The two main ICPIs are anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). The onset of kidney injury seen with PD-1 inhibitors is usually late (3-10 months) compared to CTLA-4 antagonists-related renal injury, which happens earlier (2-3 months). PD-1 inhibitors, as opposed to CTLA-4 inhibitors, have been associated with kidney rejection in transplantation. Steroids appear to be effective in treating the immune-related adverse effects noted with these agents.
References:
Izzedine H, et al. Renal effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017; 32(6):936-42.
Bottlaender L, et al. Acute interstitial nephritis after sequential ipilumumab – nivolumab therapy of metastatic melanoma. J Immunother Cancer 2017; 5(1):57.
Wanchoo R, et al. Adverse Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Narrative Review. Am J Nephrol 2017; 45(2) 160-69.
Cortazar FB, et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016; 90(3):638-47.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.