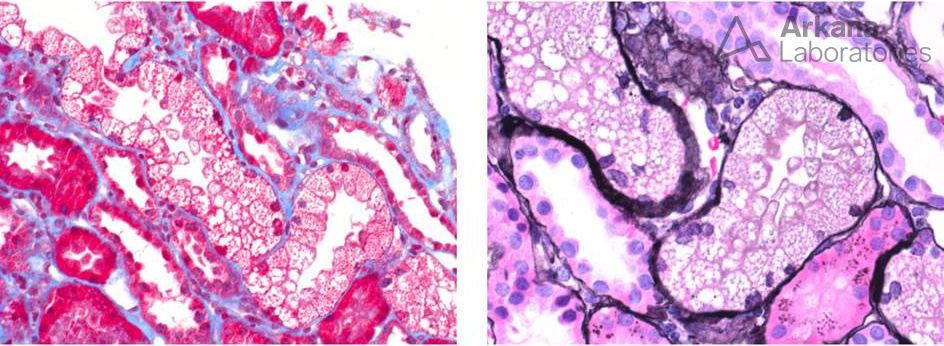
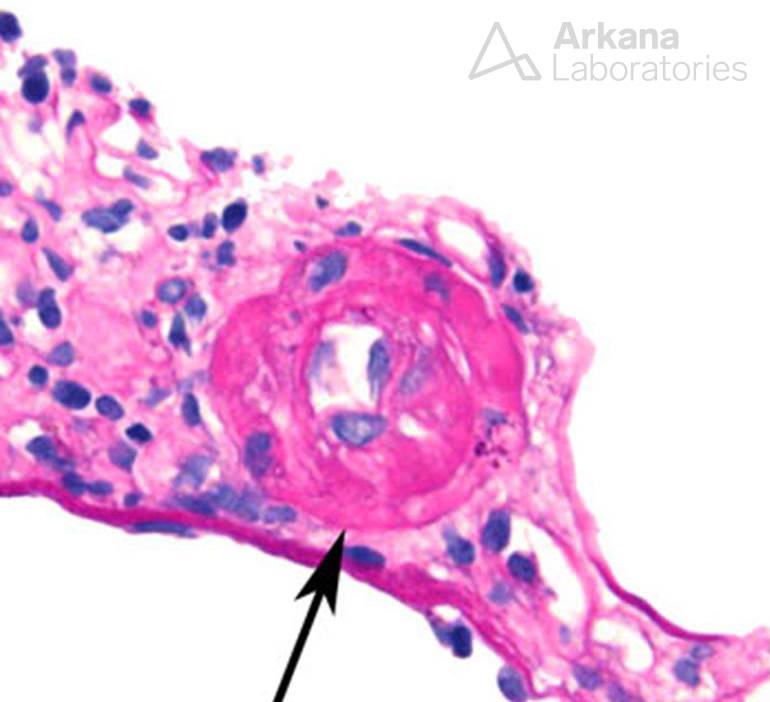
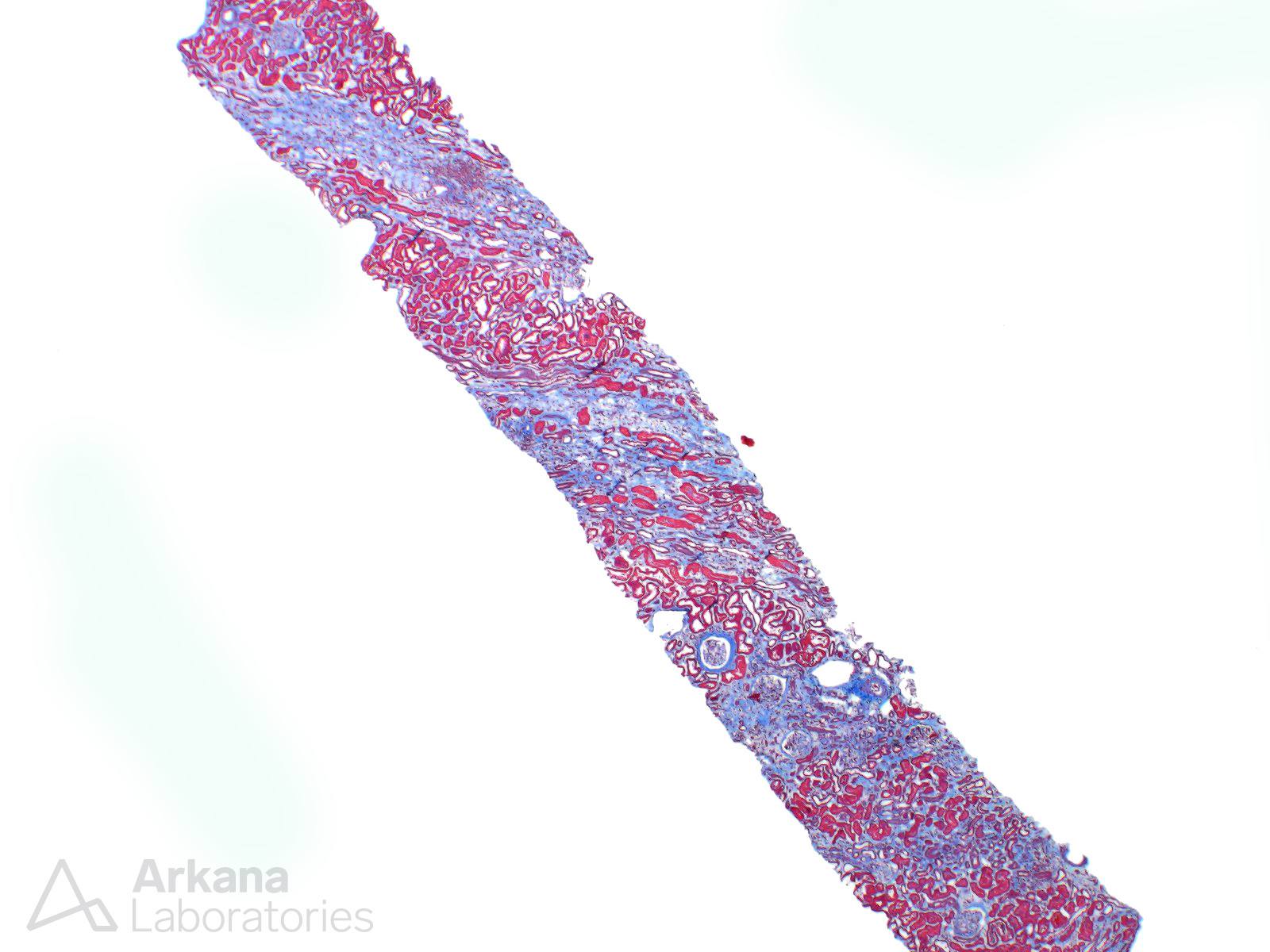
A 45 year-old man received renal transplantation for HCV-associated end stage renal disease. He is currently treated with Sofobuvir, Tacrolimus and ACEI. He developed renal function impairment (Serum Cr increased to 2.3 mg/dL) with mild proteinuria. Based on the renal biopsy images, which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Severe acute tubular injury due to Sofobuvir
B. Calcineurin inhibitor toxicity
C. Polyomavirus nephropathy
D. Tubular injury secondary to cryoglobulinemia
E. Diabetic nephropathy
The answer is B. The light microscopic examination demonstrates isometric vacuolization of tubular epithelial cells, severe hyaline arteriolopathy and a striped pattern of fibrosis. These features are suggestive of calcineurin inhibitor toxicity (CNIT)
CNIT is dose related, with variable individual susceptibility.
Histologic Features associated with CNIT:
Tubulointerstitial:
Acute: Acute tubular injury with focal isometric vacuolization of proximal tubular segments (see images)
Chronic: Striped interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy with microcalcifications
Vascular:
Acute arteriolopathy: Smooth muscle loss and expansion of intima and media by loose matrix
Chronic arteriolopathy: Nodular medial hyalinization
Acute and Chronic Thrombotic microangiopathic changes can also be seen
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.