The 3 main FSGS Types
Are there clues to help distinguish among primary, genetic, and secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) lesions?
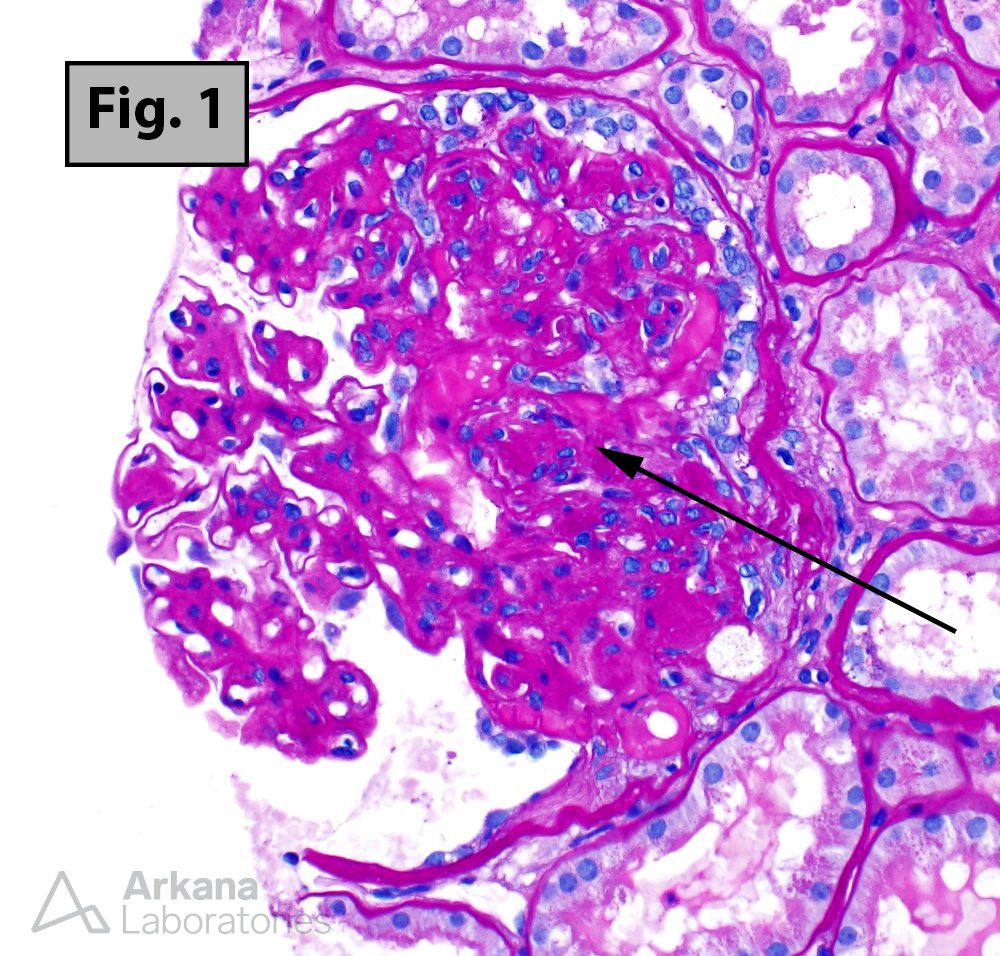
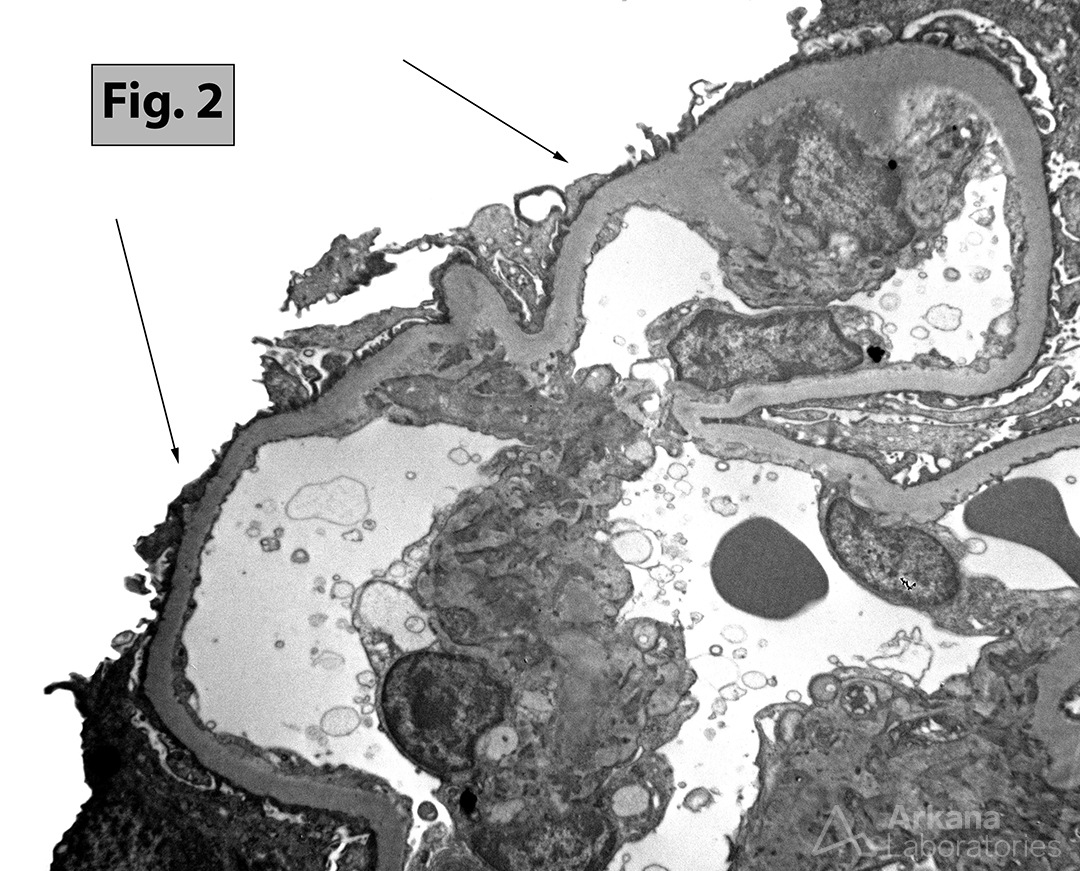
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) (Fig. 1) represents a morphologic pattern of injury rather than a specific disease. Current thinking on this important subject is thoroughly presented in a recent review by De Vriese AS, Sethi S, et al (J Am Soc Nephrol 29: 759–774, 2018). The authors discuss the three main etiologic categories of disease associated with FSGS lesions: primary FSGS, genetic FSGS, and secondary (“maladaptive”) type FSGS. The authors also emphasize the importance of determining whether the patient has nephrotic syndrome (defined by the presence of nephrotic range proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia) and using electron microscopy to assess the degree of foot process effacement. Primary FSGS, for example, is most reliably diagnosed in patients with nephrotic syndrome and severe foot process effacement (>80%) (Fig. 2). Other variations on the clinical presentation and/or pathologic findings can also help distinguish primary FSGS from FSGS caused by genetic or secondary maladaptive states.
Reference:
De Vriese AS, Sethi S, Nath KA, Glassock RJ, Fervenza FC. Differentiating Primary, Genetic, and Secondary FSGS in Adults: A Clinicopathologic Approach. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Mar;29(3):759-774. PubMed PMID: 29321142
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.